What is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting digital systems, networks, and data from cyber threats. With the increasing adoption of digital technologies, cybersecurity has become one of the most in-demand and high-paying career fields globally. Organizations across industries rely on cybersecurity professionals to prevent data breaches, cyberattacks, and regulatory violations.
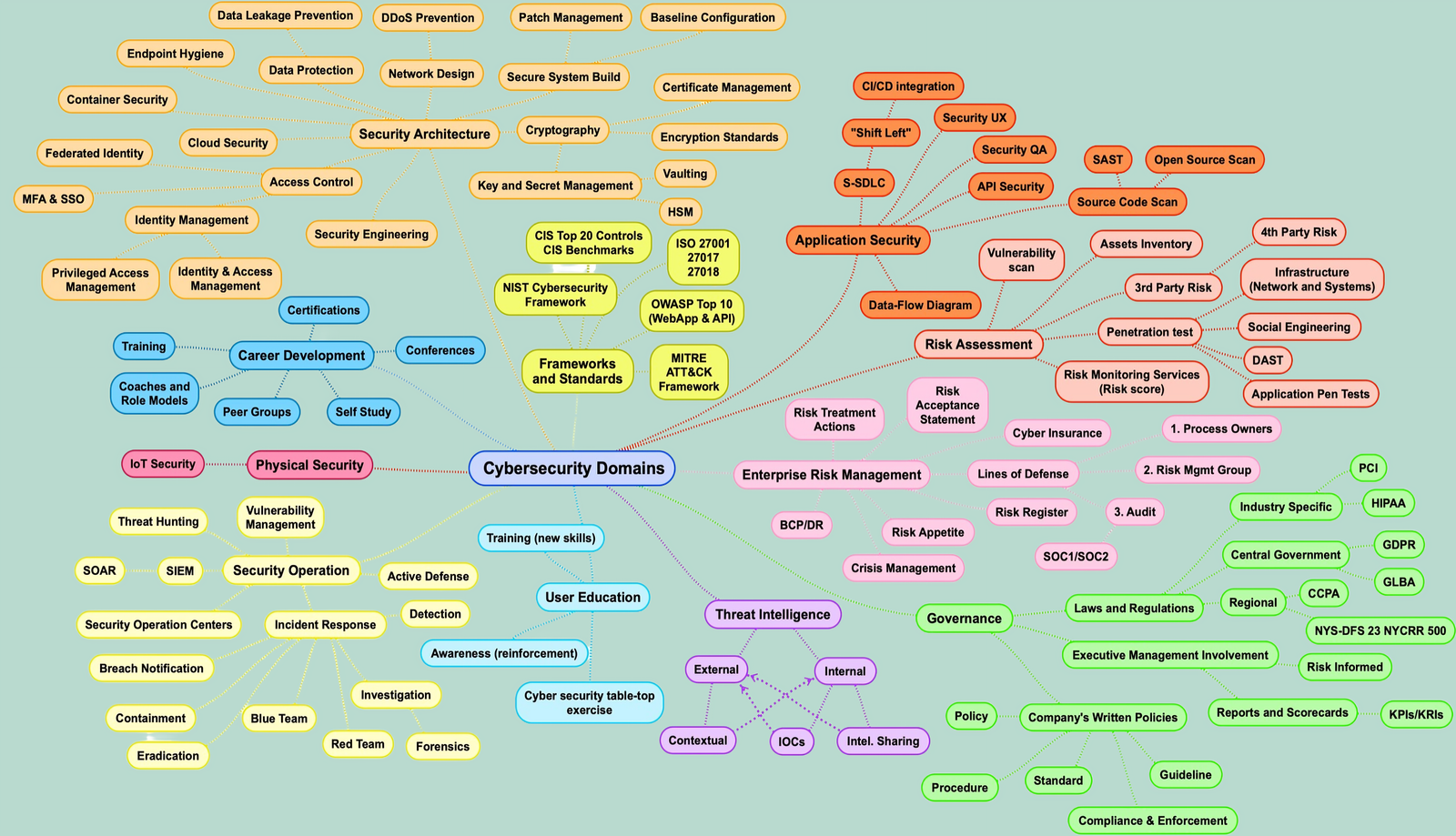
Key Domains in Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is a broad field that offers multiple career paths. Here are some of the major domains you can specialize in:
- Network Security – Protecting network infrastructure from cyber threats using firewalls, VPNs, and IDS/IPS systems.
- Cloud Security – Securing cloud-based applications, platforms, and infrastructure (AWS, Azure, Google Cloud).
- Penetration Testing & Ethical Hacking – Identifying vulnerabilities in systems and applications by simulating cyberattacks.
- Incident Response & Forensics – Investigating cyber incidents and implementing countermeasures to mitigate risks.
- Identity & Access Management (IAM) – Managing user authentication, authorization, and access controls.
- Application Security – Securing software applications through secure coding practices and vulnerability assessments.
- Industrial Control System (ICS) Security – Protecting critical infrastructure like power grids and manufacturing systems.
- Cyber Threat Intelligence (CTI) – Analyzing threat landscapes and predicting potential cyber risks.
- Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) – Ensuring regulatory compliance, managing risks, and setting security policies.
Each of these domains requires a unique skill set and technical expertise, making cybersecurity an exciting and diverse career field.
Technical Skills Required for Cybersecurity
If you’re considering a career in cybersecurity, here are the foundational technical skills you may need, depending on your chosen domain:
- Networking & Security Concepts – Understanding TCP/IP, DNS, firewalls, IDS/IPS, and VPNs.
- Operating Systems – Proficiency in Windows, Linux, and macOS security.
- Programming & Scripting – Python, Bash, or PowerShell for automation and security tasks.
- Cloud Technologies – Knowledge of AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud security practices.
- Penetration Testing Tools – Familiarity with Kali Linux, Metasploit, Burp Suite, and Nmap.
- Incident Response & Digital Forensics – Using tools like Wireshark, Splunk, and Autopsy.
- Compliance & Risk Management – Understanding frameworks like ISO 27001, NIST, SOC 2, and GDPR.
Not all cybersecurity domains require coding. For instance, GRC (Governance, Risk, and Compliance) is an area where professionals from non-technical backgrounds can transition into cybersecurity without deep technical expertise.
How GRC is Emerging as a Key Cybersecurity Domain
What is GRC?
Governance, Risk, and Compliance (GRC) focuses on establishing security policies, assessing cyber risks, and ensuring compliance with regulations like ISO 27001, NIST, GDPR, HIPAA, and SOC 2. As cybersecurity threats evolve, companies need GRC professionals to build security frameworks, assess vulnerabilities, and ensure legal compliance.
Why GRC is an Ideal Entry Point into Cybersecurity
- No Coding Required – Unlike penetration testing or ethical hacking, GRC focuses on policies, audits, and risk management, making it easier for professionals from non-IT backgrounds to enter cybersecurity.
- High Demand & Job Security – Every organization needs GRC professionals to meet compliance and reduce cyber risks.
- Cross-Industry Opportunities – GRC professionals work in healthcare, finance, government, and IT sectors.
- Fast-Track Career Growth – GRC professionals can transition into senior cybersecurity roles like Chief Information Security Officer (CISO) or Risk Manager.
Technical & Non-Technical Skills Required for GRC
Unlike technical cybersecurity roles, GRC requires a blend of business, analytical, and security skills:
Essential GRC Skills:
- Risk Assessment & Mitigation – Identifying cyber risks and recommending controls.
- Compliance & Regulatory Knowledge – Understanding frameworks like ISO 27001, NIST, GDPR, SOC 2, and PCI DSS.
- Audit & Security Frameworks – Conducting security audits and implementing compliance measures.
- Third-Party Risk Management (TPRM) – Evaluating vendor security risks.
- Communication & Documentation – Writing security policies and interacting with stakeholders.
Recommended GRC Certifications:
To enhance your credibility, consider earning industry-recognized certifications:
- ISO 27001 Lead Auditor (LA) / Implementer
- Certified in Risk and Information Systems Control (CRISC)
- Certified Information Systems Auditor (CISA)
- Certified Third-Party Risk Professional (CTPRP)
- ISO 42001 Lead Auditor (AI Governance)
How CyberGRC Troopers Helps You Build a Career in GRC & Cybersecurity
At CyberGRC Troopers, we specialize in helping professionals transition into cybersecurity through GRC. Our structured training programs make cybersecurity accessible to both technical and non-technical individuals.
Why Choose CyberGRC Troopers?
 Beginner-Friendly Courses – No prior IT or coding knowledge required!
Beginner-Friendly Courses – No prior IT or coding knowledge required! Hands-on Training – Real-world case studies, risk assessments, and policy writing exercises.
Hands-on Training – Real-world case studies, risk assessments, and policy writing exercises. Certification Preparation – We train you for globally recognized certifications like ISO 27001, CRISC, and CTPRP.
Certification Preparation – We train you for globally recognized certifications like ISO 27001, CRISC, and CTPRP. Industry-Relevant Curriculum – Learn risk management, compliance, and audit practices used by top organizations.
Industry-Relevant Curriculum – Learn risk management, compliance, and audit practices used by top organizations. Job Assistance & Career Guidance – Resume building, interview preparation, and job referrals.
Job Assistance & Career Guidance – Resume building, interview preparation, and job referrals.
Start Your Cybersecurity Journey Today!
Cybersecurity is a vast field with multiple career paths. If you are looking to transition into cybersecurity without coding, GRC is the perfect entry point. With structured training from CyberGRC Troopers, you can gain the necessary skills and certifications to land a high-paying cybersecurity job.
 Contact CyberGRC Troopers today and take the first step towards a rewarding cybersecurity career!
Contact CyberGRC Troopers today and take the first step towards a rewarding cybersecurity career!